Hydraulic Accumulators Cost Savings Stable Pressure Waterjet Pump Parts In Stock
Hydraulic Accumulators Cost Savings Stable Pressure Waterjet Pump Parts In Stock

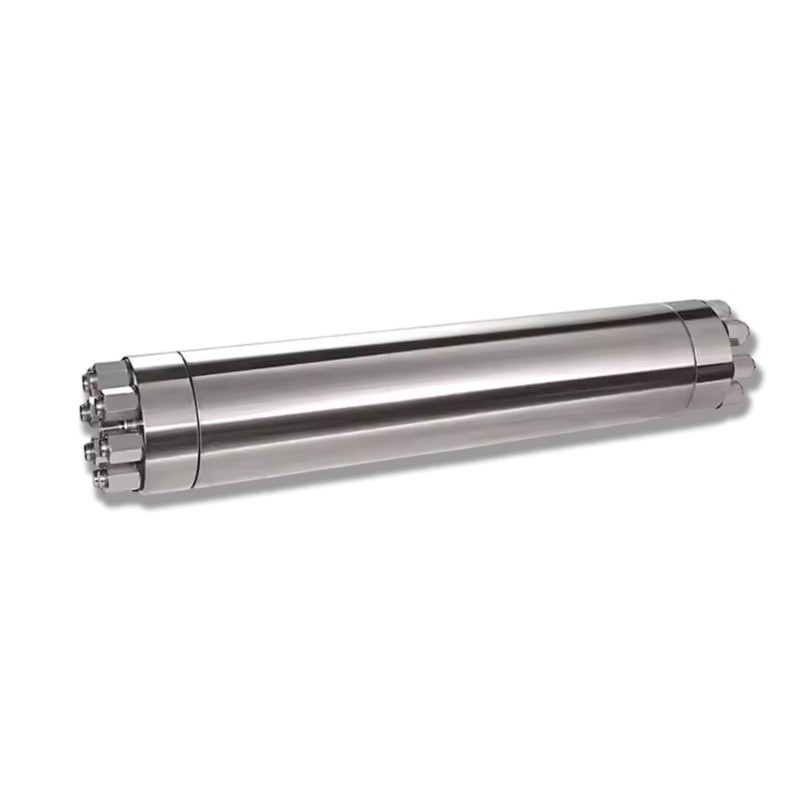
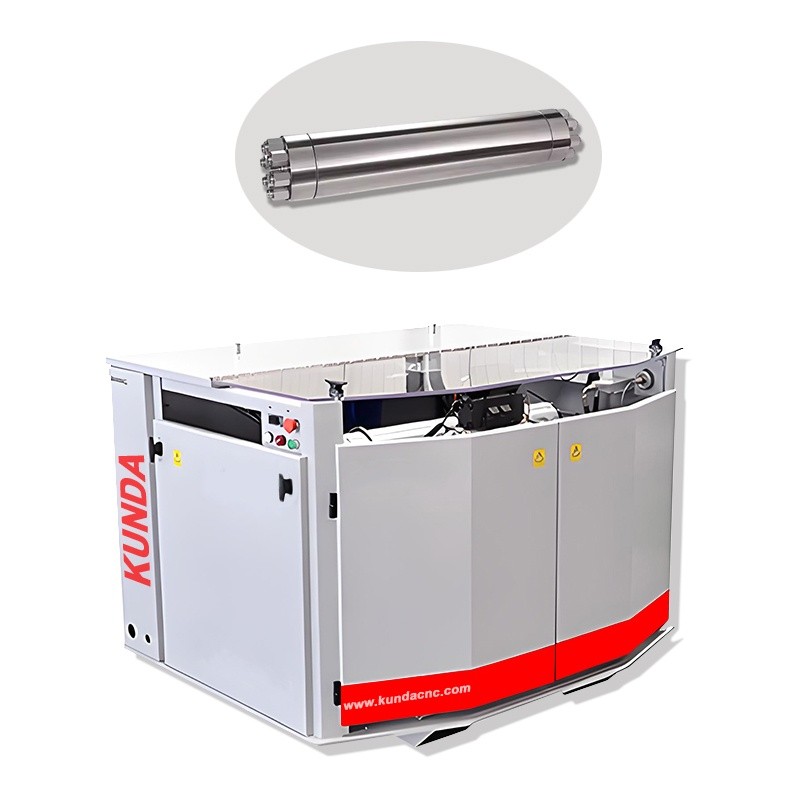
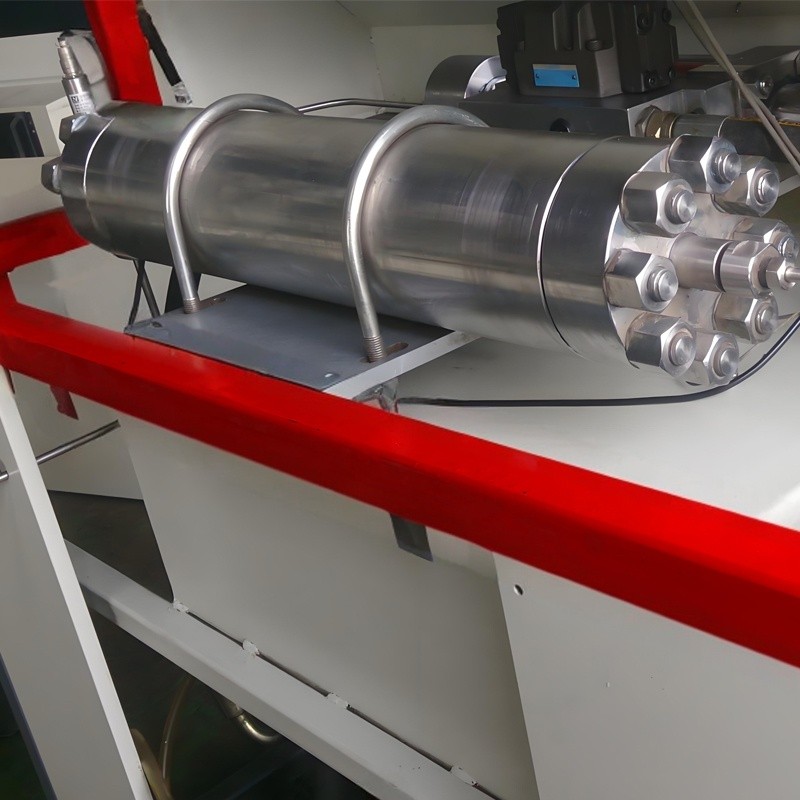
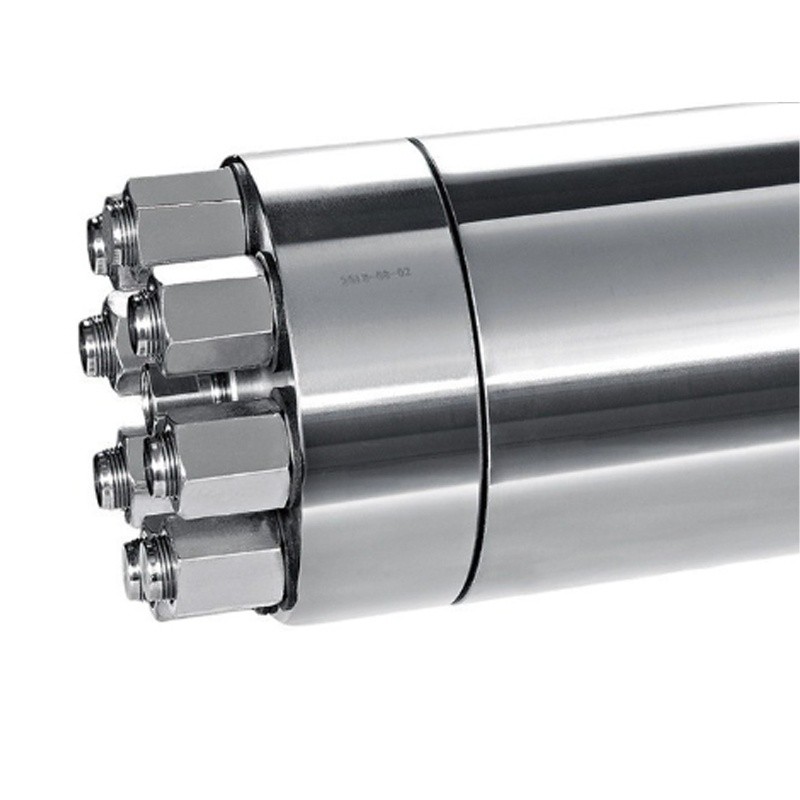
The Hydraulic Accumulators is an indispensable core component in the Waterjet Cutting System. It is mainly used to store the liquid pressure energy generated by the high-pressure water flow and release it stably during the cutting operation to form a continuous, high-speed Water Jet to achieve precise cutting.
| Name |
Hydraulic Accumulators |
| Material | Stainless Steel |
| Application | Waterjet Intensifier Pump |
| Type | Waterjet Pump Parts |
| MOQ | 1SET |
| Capacity | 1L/1.4L/2L/2.5L |
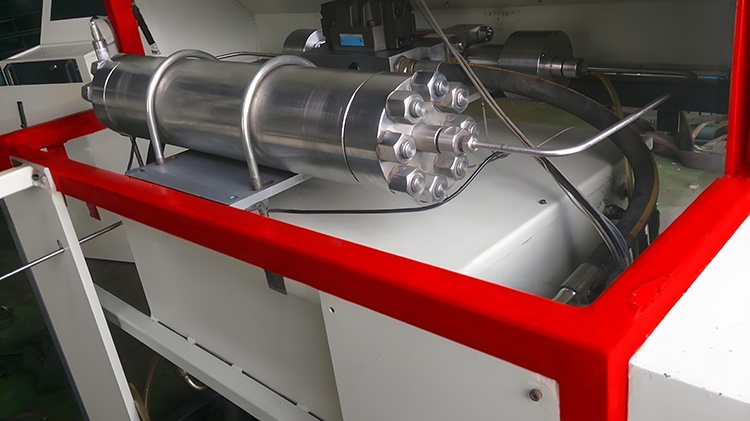

Main function Hydraulic Accumulators
Stabilize pressure: The reciprocating motion of the booster piston will cause pressure fluctuations. The accumulator eliminates pressure pulsation by buffering and releasing the stored energy, providing a smooth and continuous water flow.
Energy storage and compensation: Store excess energy at the peak of system pressure, and release it when the pressure drops or leaks to maintain constant high pressure and prevent cutting interruption.
Improve cutting efficiency: Large-capacity accumulators can extend the pressure peak maintenance time, avoid peaks and troughs, ensure uniform water jet speed, and are suitable for hard material cutting.
Key features and selection Hydraulic Accumulators
Capacity requirements: Selecting a large-capacity accumulator (such as matching according to cutting requirements) can better suppress pressure attenuation and optimize cutting effects; for example, mixed sand cutting often uses large-capacity designs to maintain high pressure.
Material and maintenance: The accumulator cylinder needs to be made of high-strength, corrosion-resistant materials (such as special alloys) and adopt a maintenance-free structure (such as canceling the soft seal design) to extend the service life.
System matching: The pressure and capacity of the Hydraulic Accumulators need to be coordinated with the Booster Pump and nozzle aperture (such as 0.08–0.45mm) to avoid reduced efficiency due to parameter mismatch.